Cryptocurrency Posts
Crypto Briefing
The long-term accumulation trend among crypto ETF investors suggests a stabilizing influence on the volatile crypto market landscape.
The post BlackRock says over 90% of Bitcoin ETF investors are long-term accumulators appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
Musk's restructuring of xAI highlights challenges in leadership transitions and the impact of aggressive management on company morale and talent retention.
The post Elon Musk removes more xAI founders during restructuring ahead of potential IPO appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
The launch of Velotrade's crypto prop platform could democratize access to capital for traders, potentially reshaping the crypto trading landscape.
The post Ex-JP Morgan and Dresdner Kleinwort traders launch crypto prop platform appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
Bitcoin's resilience amid economic uncertainty suggests a potential shift in its role as a hedge, but market sentiment remains cautious.
The post Bitcoin holds steady as inflation stays sticky and growth slows appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
The postponement underscores the impact of geopolitical instability on global events, highlighting the need for adaptive planning in volatile regions.
The post TOKEN2049 Dubai postponed to April 2027 amid regional security concerns appeared first on Crypto Briefing.
Bitcoin Magazine
Bitcoin Magazine

AI Pivot Won’t Save Everyone, Wintermute Tells Bitcoin Miners
Bitcoin miners are caught in the tightest squeeze of the network’s history, and a new Wintermute report argues that simply waiting for the next bull run is no longer a strategy.
Instead, the firm says miners will have to reinvent themselves as infrastructure and treasury managers if they want to make it to the next halving.
Wintermute analyst Jasper De Maere says the current mining cycle is structurally different from prior ones in 2018 and 2022. Bitcoin’s design cuts block rewards in half every four years, but this time the price has not doubled over the same window, which means miner revenue is shrinking in real terms.
On a rolling four‑year basis, Bitcoin has only returned about 1.15x in this epoch, far below the 10x–20x multiples seen in earlier cycles.
In past cycles, huge price gains covered up a lot of problems. Miners could count on bull markets to bail out weak margins after each halving.
Today, with institutions, ETFs, and corporate treasuries in the mix, Bitcoin trades more like a mainstream macro asset, and those explosive 20x runs are less likely.
For miners that built their business on the assumption of permanent hypergrowth, Wintermute frames this as a regime change, not a bad quarter.
Margins are getting crushed
Under the hood, Bitcoin mining has a very simple cost structure: energy and compute. That simplicity means there are not many ways to protect profits when revenue falls. Wintermute’s analysis shows gross margins in this epoch peaked around 30%, a level that marked the bottom during prior bear markets, not the top.
Earlier epochs saw long stretches where miners enjoyed 70–80% margins; now, the “good times” look more like prior stress points.
Transaction fees are not saving the day either. Fee spikes tied to hype cycles and mempool congestion show up on charts, but they fade fast and rarely contribute more than a few percent of total miner revenue over time.
Wintermute notes that even when you include fees, the margin lines for each cycle barely move apart, especially in the current epoch. In other words, the protocol’s built‑in “second revenue stream” is not acting as a reliable backstop.
The AI pivot is an opportunity for a few
One path out of the squeeze is getting plenty of attention: pivoting into high‑performance computing (HPC) and AI workloads. Big tech firms and AI startups are racing to lock in power and data center capacity, and they do not want to wait five to ten years for new grid connections and construction.
Miners, who already control cheap power and built‑out sites, are a natural shortcut.
Wintermute points out that sites once valued at roughly 1–7 dollars per watt as pure mining operations have changed hands at close to 18 dollars per watt after being repositioned for AI compute, helped by deals like HUT’s work with Google and Anthropic.
Public‑market investors have rewarded miners that announce credible AI plans with higher valuations and cheaper capital through equity and convertible debt.
The catch is that not every miner has the location quality, balance sheet, or operational capacity to turn into a data‑center business.
Putting “idle” Bitcoin to work
That is where Wintermute sees a second, underused lever: active balance sheet management. Miners together hold close to 1% of all Bitcoin, a legacy of the “HODL” playbook that dominated earlier cycles.
At the same time, many listed miners have been selling down parts of their treasuries to cover tighter margins and debt, with some even wiping out holdings altogether.
Instead of letting reserves sit idle until they are dumped in a liquidity crunch, Wintermute argues miners should treat BTC like a working asset. On the “active” side, that means using derivatives strategies such as covered calls and cash‑secured puts to earn yield on holdings, at the cost of taking some market risk.
On the “passive” side, miners can deploy coins into on‑chain lending markets, including a new wrapped‑BTC market on Wildcat that Wintermute has highlighted, to generate interest income.
Wintermute’s bottom line is that Bitcoin’s design is working, but the easy era for miners is over. Difficulty can still adjust, yet it cannot overcome slower price growth, a fee market that has not scaled, and rising energy costs that eat into every block reward.
The AI pivot will likely reshape the upper tier of the industry, turning some miners into full‑blown infrastructure companies.
This post AI Pivot Won’t Save Everyone, Wintermute Tells Bitcoin Miners first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

South African Eskom Considering Discount Power for Bitcoin Miners as Solar Creates Surplus
Eskom, a South African electricity public utility, is exploring plans to sell excess daytime electricity to Bitcoin mining companies as rooftop solar installations reduce grid demand during daylight hours.
Speaking at the Biznews Conference 2026 in Hermanus, Eskom chairman Mteto Nyati said the utility is evaluating ways to monetize surplus power generated during the middle of the day, according to local reporting.
South Africa’s rapid adoption of rooftop solar systems has begun to reshape the country’s electricity demand profile. Many households and businesses now generate their own power during daylight hours, leaving Eskom with unused capacity once solar panels begin producing electricity.
Nyati said the pattern is increasingly predictable.
Demand spikes in the early morning as households prepare for work and businesses open. As solar generation ramps up later in the day, grid demand falls, leaving Eskom with surplus electricity.
Eskom is looking at creative ways and means of using that capacity. One option under review is offering discounted electricity to Bitcoin mining companies operating in South Africa. The sector runs large data centers that perform energy-intensive computations to secure the Bitcoin network.
Nyati said industries such as Bitcoin mining are contributing to rising global electricity demand. He said that the technology did not exist two decades ago but now represents a growing source of power consumption.
Selling excess electricity to miners could allow Eskom to generate revenue from power that might otherwise go unused during solar-heavy hours.
South African Bitcoin mining opportunities
The idea also builds on earlier comments from Eskom chief executive Dan Marokane, who said the state-owned utility is examining opportunities tied to Bitcoin mining, artificial intelligence infrastructure, and large-scale data centers.
Those sectors require large, continuous electricity supplies and could provide new demand for Eskom’s generation fleet.
Nyati framed the initiative as part of a broader strategy to adapt to structural changes in South Africa’s electricity market.
The country’s power sector is opening to private investment, allowing independent companies to build generation capacity and compete in electricity distribution. At the same time, rising rooftop solar adoption is shifting demand away from the national grid.
Nyati said Eskom must adapt to remain viable in a more competitive environment.
Alongside new revenue strategies, Eskom is pursuing cost reductions. Nyati said the utility plans to eliminate about R112 billion in expenses over the next five years.
Reducing those costs could help lower electricity prices for households and energy-intensive industries such as mining and smelting.
Despite the changes in the energy landscape, Nyati said South Africa still needs a strong national utility.
He argued that Eskom’s coal and nuclear power stations provide the base-load electricity required to support industrial growth and economic development.
The proposal to supply discounted electricity to Bitcoin miners reflects how utilities are beginning to treat flexible energy consumers as tools for balancing supply and demand in an evolving power system.
This post South African Eskom Considering Discount Power for Bitcoin Miners as Solar Creates Surplus first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

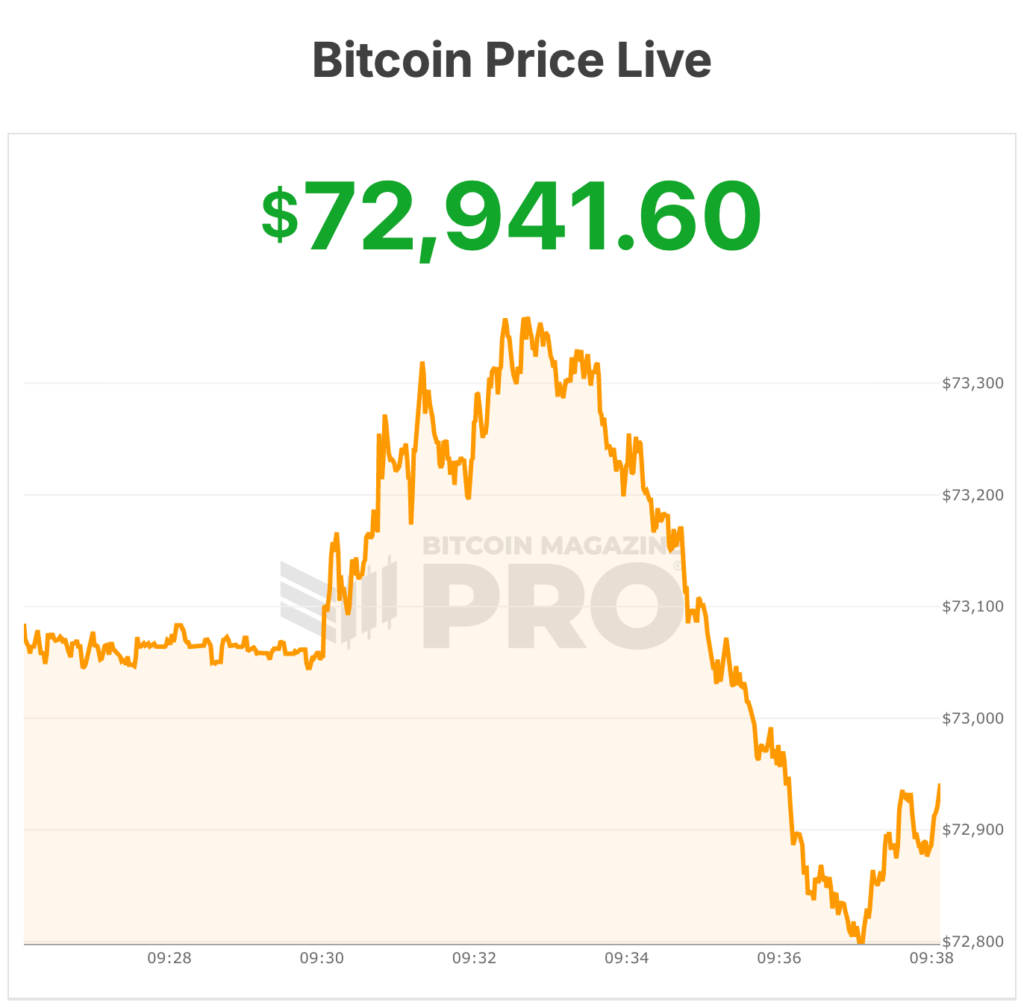
Bitcoin Price Reclaims $73,000 as War Shakes Markets, Outperforming Gold and Stocks
The Bitcoin price has outperformed gold, silver, and major U.S. equity indexes since the outbreak of the Iran–Israel conflict escalation 2026, climbing above $73,000 even as oil surged and expectations for near-term interest rate cuts faded.
Market data shows Bitcoin price rising about 8% since the first strikes against Iran, reaching a one-month high above $73,000. The move placed the digital asset ahead of several traditional safe-haven and risk assets during a period of geopolitical stress.
Gold declined during the same stretch, falling roughly 3% from levels seen before the conflict began. Silver dropped more than 10%, sliding from above $90 to around $82. U.S. equities also weakened, with the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq Composite each down between 1% and 2%.
The divergence came as global markets responded to a surge in energy prices. Crude oil climbed close to 20%, breaking above $100 per barrel for the first time in nearly four years as tensions threatened supply routes across the Middle East.
These conditions often pressure crypto markets because higher oil prices and tighter financial conditions raise inflation concerns and reduce risk appetite across global portfolios.
The bitcoin price followed that pattern at first.
In the hours after the conflict began, the asset dropped sharply as traders cut exposure across crypto derivatives markets. Roughly $300 million in leveraged positions were liquidated during the initial weekend selloff. Bitcoin briefly fell toward the mid-$63,000 range as uncertainty spread through global markets.
The selloff matched Bitcoin’s historical behavior during geopolitical shocks, where it often trades in line with other high-beta assets during the first wave of risk reduction.
The market response changed during the following week.
Bitcoin price recovery
Instead of remaining near those lows while energy prices climbed, Bitcoin price recovered steadily and broke back above the $70,000 level. The rebound left it outperforming metals and equities during the same window despite the challenging macro backdrop.
Derivatives data via Bitcoin Magazine Pro shows that part of the recovery followed a reset in market leverage. After the liquidation event cleared large speculative positions, traders began rebuilding exposure.
Open interest across major exchanges climbed back to roughly 88,000 BTC. The increase signals renewed participation without reaching extreme leverage levels that often precede sharp corrections.
Institutional demand also contributed to the rebound.
U.S. spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds recorded strong inflows during the week. Data from ETF trackers shows the funds attracted about $586 million, marking one of the largest inflow weeks of the year.
The flows represent a steady source of demand entering the market even as geopolitical tensions intensified and inflation concerns returned.
Robert Mitchnick, head of digital assets at BlackRock, said the behavior of ETF investors has remained stable during periods of volatility.
Speaking on CNBC, Mitchnick said ETF flows show a long-term accumulation pattern even during large price declines in Bitcoin price.
He said the investor base across financial advisors, institutions, and direct retail buyers has taken a steady approach to the asset, with many participants using price weakness to add exposure.
He also pointed to the performance of the iShares Bitcoin Trust ETF (IBIT), which continued attracting inflows despite a sharp drop in Bitcoin’s price from its previous peak.
Mitchnick said IBIT ranked among the largest ETF inflows globally during 2025 even while the underlying asset declined, highlighting sustained demand from long-term investors.
The growth of spot ETFs has expanded Bitcoin’s investor base and deepened market liquidity compared with earlier geopolitical episodes. Institutional capital can now enter the market through regulated products that trade alongside equities.
For now, Bitcoin’s performance during the conflict has reinforced its status as a liquid macro asset that reacts to both global market forces and crypto-native demand.
While oil, inflation expectations, and central bank policy continue to shape the backdrop, the digital asset has managed to recover faster than many traditional benchmarks during one of the most volatile geopolitical episodes of the year.
At the time of writing, Bitcoin price is trading at $72,941.
This post Bitcoin Price Reclaims $73,000 as War Shakes Markets, Outperforming Gold and Stocks first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

Strategy (MSTR) Bought Over 4,000 Bitcoin Today via STRC As Strong Week Continues
Strategy appears to have purchased more than 4,000 bitcoin on Thursday, according to estimates derived from real-time trading data and community tracking dashboards monitoring the firm’s preferred equity sales.
Data from STRC.live and market trackers suggests the purchases were funded through heavy issuance of the company’s Variable Rate Series A Preferred Stock (STRC), a perpetual preferred instrument that Strategy has increasingly used to raise capital for bitcoin accumulation.
By end of day in New York, trading activity implied the firm had already raised enough capital to acquire more than 4,000 BTC, marking the largest single-day bitcoin purchase funded through STRC since the instrument launched.
The surge follows unusually strong activity earlier in the week. On March 10, STRC recorded a record $409 million in daily trading volume while maintaining roughly 3% 30-day volatility and a one-month volume-weighted average price near $99.78.
On-chain indicators and community monitoring suggested that day’s activity funded the purchase of more than 2,000 BTC, already one of the largest one-day accumulations tied to the instrument.
Thursday’s pace easily surpassed that figure.
Strategy, already the largest public corporate holder of bitcoin, has increasingly leaned on its preferred equity program to finance additional acquisitions.
Earlier this year the company amended its at-the-market (ATM) program, allowing multiple agents to sell STRC shares simultaneously. The change increased liquidity in the instrument and made it easier for Strategy to raise large amounts of capital quickly, with proceeds directed toward bitcoin purchases.
Real-time dashboards tracking STRC trading attempt to estimate how many shares Strategy itself is issuing versus secondary market trades.
Because the company previously indicated it may sell shares when the price trades above its $100 stated amount, analysts can approximate capital raised when trading occurs above that threshold.
A recent SEC filing disclosed that the company purchased 17,994 BTC between March 2 and March 8 for approximately $1.28 billion. That acquisition lifted the firm’s total holdings to about 738,731 BTC, representing roughly 3.5% of bitcoin’s circulating supply.
The filing showed the purchase was funded through a combination of $377.1 million in STRC sales and $899.5 million raised through common stock issuance.
Based on those figures, STRC accounted for about 29.5% of the funding for that five-day accumulation period, equivalent to roughly 5,300 BTC acquired through preferred share sales.
If Thursday’s estimates prove accurate, the day’s purchases alone could exceed the average daily bitcoin acquisition pace seen during that earlier buying window.
The data remains unofficial. Strategy typically confirms purchases later through SEC filings or public disclosures.
How does Strategy’s STRC work?
STRC acts as a bridge between traditional income investors and Strategy’s Bitcoin-focused balance sheet. Income investors typically seek steady payouts, while Strategy’s large Bitcoin holdings bring long-term upside along with short-term price swings. The preferred stock helps connect these two profiles.
The security is structured to keep demand near its $100 par value while paying a monthly dividend that yields about 11.5% annually. In effect, it converts the economics of a Bitcoin treasury into a format that appeals to fixed-income investors who prioritize regular income.
Strong liquidity and relatively low volatility suggest that the investor base is shifting toward income-focused capital. That shift can help stabilize trading activity compared with instruments driven mainly by speculation.
These early results point to product-market fit. Rather than relying on marketing or hype, the structure appears to meet a clear demand among investors seeking yield tied to Bitcoin exposure.
For corporate leaders considering Bitcoin treasury strategies, STRC offers a way to integrate Bitcoin into broader capital structures. It allows companies to draw funding from multiple investor groups while building a shared strategic reserve around the asset.
At the time of writing, Bitcoin trades near $70,000, while shares of MicroStrategy (MSTR) are down about 0.75% on the day.

This post Strategy (MSTR) Bought Over 4,000 Bitcoin Today via STRC As Strong Week Continues first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Micah Zimmerman.
Bitcoin Magazine

David Bailey Confirmed As A Bitcoin 2026 Speaker
David Bailey has been officially confirmed as a speaker at Bitcoin 2026, returning to the conference he helped build to share his perspective on Bitcoin’s expanding role across media, capital markets, and corporate strategy. As the Chairman and CEO of Nakamoto Inc. (NASDAQ: NAKA), Bailey has executed one of the most ambitious consolidation plays in Bitcoin’s history — bringing together BTC Inc., and UTXO Management under a single publicly traded Bitcoin operating company. His vision extends far beyond media: Nakamoto is positioned as a diversified Bitcoin enterprise spanning asset management, advisory services, and institutional infrastructure, with Bitcoin accumulation at its core.
Bailey has long been a central force in shaping how the global Bitcoin community organizes, communicates, and grows. Under his leadership, BTC Inc. became the parent company of Bitcoin Magazine — the longest-running source of Bitcoin news and commentary, first published in 2012 — while also building The Bitcoin Conference into the largest Bitcoin event series in the world, drawing more than 67,000 attendees across U.S., Asia, Europe, and Middle East events in 2025 alone. His work through Bitcoin for Corporations has further accelerated institutional adoption, connecting over 40 member companies with the education and networks needed to integrate Bitcoin into their treasuries.
With the Nakamoto acquisition of BTC Inc. and UTXO now complete, Bailey arrives at Bitcoin 2026 at a defining moment — not just for his own company, but for the broader Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin Magazine is published by BTC Inc, a subsidiary of Nakamoto Inc. (NASDAQ: NAKA)
Bitcoin 2026 Returns to Las Vegas Bigger Than Ever
Bitcoin 2026 will take place April 27–29 at The Venetian, Las Vegas, and is expected to be the biggest Bitcoin event of the year.
Focused on the future of money, Bitcoin 2026 will bring together Bitcoin builders, investors, miners, policymakers, technologists, and newcomers from around the world. The event will feature a wide range of pass types, including general admission passes designed specifically for those new to Bitcoin, alongside premium passes for professionals, enterprises, and institutions.
With multiple stages, immersive experiences, technical workshops, and headline keynotes, Bitcoin 2026 is designed to serve both first-time attendees and long-time Bitcoiners shaping the next era of global adoption.
Past Bitcoin Conferences in the U.S.
Bitcoin’s flagship conference has scaled dramatically over the past five years:
- 2021 – Miami: 11,000 attendees
- 2022 – Miami: 26,000 attendees
- 2023 – Miami: 15,000 attendees
- 2024 – Nashville: 22,000 attendees
- 2025 – Las Vegas: 35,000 attendees
 Get Your Bitcoin 2026 Pass
Get Your Bitcoin 2026 Pass
Bitcoin Magazine readers can save 10% on Bitcoin 2026 tickets using code ‘ARTICLE10‘ at checkout.
Stay at The official hotel of Bitcoin 2026, The Venetian, and get a guaranteed low rate plus 15% off your pass. Be in the middle of where the fun is all happening, and where the networking never ends.
Bring your whole team to Bitcoin 2026 and get 20% off your entire order, bring more than six in a group and get 25% off for a limited time.
Volunteer at Bitcoin 2026 and get Pro Pass access plus exclusive perks.
 Location: The Venetian, Las Vegas
Location: The Venetian, Las Vegas Dates: April 27–29, 2026
Dates: April 27–29, 2026
With tens of thousands of attendees expected and hundreds of major speakers like David Bailey already confirmed, now is the time to lock in your ticket.
Buy Bitcoin 2026 Tickets — Save 10%
Why Attend Bitcoin 2026?
Bitcoin 2026 is the definitive gathering for anyone serious about the future of money. With 500+ speakers, multiple world-class stages, and programming spanning Bitcoin fundamentals, open-source development, enterprise adoption, mining, energy, AI, policy, and culture, the conference brings every corner of the Bitcoin ecosystem together under one roof.
From headline keynotes on the Nakamoto Stage to deep technical sessions for builders, institutional strategy discussions for enterprises, and beginner-friendly Bitcoin 101 education, Bitcoin 2026 is designed for everyone—from first-time attendees to the leaders shaping Bitcoin’s global adoption.
Whether you’re looking to learn, build, invest, network, or influence, Bitcoin 2026 is where Bitcoin’s next chapter is written.
Bitcoin 2026 Pass Types: Something for Everyone
Bitcoin 2026 offers a range of pass options designed to meet the needs of newcomers, professionals, enterprises, and high-net-worth Bitcoiners alike.
 Bitcoin 2026 General Admission Pass
Bitcoin 2026 General Admission Pass
Ideal for newcomers and those looking to experience the heart of the conference.
- Limited access on Days 2 & 3
- Entry to Main Stage
- Access to Genesis Stage
- Full access to the Expo Hall

 Bitcoin 2026 Pro Pass
Bitcoin 2026 Pro Pass
Designed for professionals, operators, and serious Bitcoin participants.
Includes all General Admission features, plus:
- Full 3-day access, including Pro Day
- Entry to the Pro Pass Reception
- Access to Enterprise Hall, Enterprise Stage, and Networking Lounge
- Conference App networking features
- Access to the Bitcoin For Corporations Symposium
- Entry to Compute Village and Energy Stage
- Complimentary lunch, coffee, tea, and snacks
- Dedicated registration and check-in
- Reserved seating at Main Stage
- Huge savings when you bundle your hotel and Pro Pass

 Bitcoin 2026 Whale Pass
Bitcoin 2026 Whale Pass
The all-inclusive, premium Bitcoin 2026 experience.
Includes all Pro Pass features, plus:
- Reserved seating at Main Stage
- All-inclusive gourmet food and beverages
- Entry to Whale Night and Whale Reception
- Access to all official after-parties
- Networking app access to connect with other Whales
- Premium access to The Deep — an exclusive networking lounge with intimate speaker sessions
- Complimentary stay at The Venetian when you bundle your whale pass and hotel (use promo code ‘WHALEHOTEL’ here)
This is the most immersive way to experience Bitcoin 2026.

 Bitcoin 2026 After Hours Pass
Bitcoin 2026 After Hours Pass
Your ticket to the night.
Most deals are done with a drink in your hand. Get exclusive access to 3 official Bitcoin 2026 after-parties across Las Vegas — each with a 2-hour open bar — where the real conversations happen and the best connections are made.
- Access to 3 official Bitcoin 2026 after-parties
- 2-hour open bar at each event
- Evening events across Las Vegas, April 27–29
- Network with Bitcoiners, builders, and industry leaders after hours

More headline speaker announcements are coming soon.
Don’t miss Bitcoin 2026.
This post David Bailey Confirmed As A Bitcoin 2026 Speaker first appeared on Bitcoin Magazine and is written by Jenna Montgomery.
CryptoSlate
A quiet shift is underway in the stablecoin hierarchy. While Tether’s USDT still dominates the digital dollar market, the gap between the two largest issuers is narrowing as USDC steadily expands its footprint and Tether’s growth shows signs of softening.
Additionally, USDC is gaining ground in the places where the next wave of crypto money is likely to show up most clearly: regulated payments, institutional settlement, and high-velocity on-chain transfers.
Tether’s USDT still holds the largest stock of digital dollars in circulation, but the contest is shifting from a simple market-cap race to a fight over which issuer controls the rails that move new capital through crypto.
That split is now visible in both the long-term structure and the last month of market-cap movement. The stablecoin market stands at about $315 billion, giving the sector a much larger base than earlier in the cycle.
Within that pool, USDT still leads with 58% market share by supply, keeping Tether firmly in command of the largest crypto cash reserve.
Supply, however, is only one part of the picture. The more revealing question is where fresh dollars are going, which token they move through, and which issuer is building infrastructure institutions can use at scale.
That is where Circle has started to build a stronger case. Circle's financial statements confirm USDC circulation reached $75 billion at the end of 2025, up 72% year over year, while Q4 on-chain transaction volume climbed to $12 trillion, up 247% from a year earlier. Those figures indicate a stablecoin moving through wallets, venues, and payment flows more quickly.
Tether, for its part, remains too large to dismiss. In its latest quarterly disclosure, Tether stated USDT circulation topped $186 billion, reserve assets approached $193 billion, and its total US Treasury exposure reached $141 billion.
It also said it issued nearly $50 billion in new USDT during 2025. Those figures show a business that still dominates the inventory side of crypto dollars, especially across exchanges, offshore trading venues, and markets where users want a dollar-linked asset without relying on local banking systems.
Over the past month, USDC’s market cap has risen around 8%, pushing it to roughly $79 billion and a fresh all-time high.
Tether has remained far larger, but USDT is still sitting about $3 billion below the roughly $187 billion peak it reached in December 2025, a gap that gives Circle a clearer opening to chip away at Tether’s lead than the headline supply table alone suggests.
So the tension is real. Tether still controls the biggest pile of crypto cash. Circle is building faster in the parts of the market most closely aligned with the next phase of regulation and institutional adoption.
For traders and Bitcoin investors, stablecoins remain the main form of dollar liquidity inside crypto.
Whoever captures more of the next inflow can shape where liquidity thickens, how collateral is posted, and which rails become the default path for new capital entering the market.
USDT still owns supply, while USDC is winning more of the flow
The cleanest way to understand the shift is to separate supply from velocity. USDT still leads in outstanding supply, meaning more dollars are parked in Tether than in any rival stablecoin. But transaction data suggests USDC is gaining influence over how money moves.
Bloomberg, citing Artemis Analytics, reported that stablecoin transaction volume rose 72% to $33 trillion in 2025, with USDC accounting for $18.3 trillion and USDT for $13.3 trillion.
That divergence carries more weight than a simple supply table. A stablecoin that wins more transaction flow can become the preferred medium for settlement, treasury movement, and short-duration capital rotation, even while another token still holds a larger long-term balance.
Put differently, Tether still looks stronger as stored crypto cash, while Circle is making a case to become the preferred token for moving crypto cash.
The market is also assigning the two issuers different jobs. Tether’s edge remains distribution. It has the deepest footprint across global exchanges and a large user base in emerging markets, where demand for dollar-linked assets often reflects local currency weakness, capital controls, or banking friction.
Circle’s edge is legibility. It has built a reserve model and disclosure framework that fit more naturally with banks, regulated payment firms, and institutions that need cleaner lines around custody, compliance, and audits.
Circle’s own transparency page makes that pitch directly. The company says the bulk of USDC reserves sit in the BlackRock-managed Circle Reserve Fund, with the rest primarily in cash at regulated financial institutions, and notes that its financial statements are audited by Deloitte.
That does not erase market competition, and it does not guarantee that USDC will overtake USDT by supply. It does give Circle a stronger position in the regulated lane of the market at a moment when regulation is beginning to sort winners by use case.
The policy backdrop is moving in that direction. A Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis review of the GENIUS Act framework says payment stablecoin issuers face tight reserve rules, monthly disclosures, and annual audited financial statements once issuance passes $50 billion.
State-qualified issuers above $10 billion would also need to move toward federal oversight within a year. Those thresholds do not decide the market on their own, but they make compliance architecture more important than it was during the earlier, more crypto-native phase of stablecoin growth.
| Metric | USDT | USDC | Why it is relevant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circulation / supply | $183 billion | $79 billion | Shows where the largest stock of crypto dollars sits |
| 2025 issuance / growth | Nearly $50 billion new issuance in 2025 | 72% year-over-year circulation growth | Shows how quickly each issuer is expanding |
| Transaction volume in 2025 | $13.3 trillion | $18.3 trillion | Shows which token is moving more money |
| Core strategic edge | Exchange distribution and global trading liquidity | Regulated settlement and institutional usability | Points to a split market rather than a single winner |
That split is already visible in payments. Visa launched USDC settlement in the United States with Cross River Bank and Lead Bank and plans broader U.S. expansion through 2026. It also said its monthly stablecoin settlement volume had reached a $3.5 billion annualized run rate as of November 30.
That is not the same as saying USDC will dominate all crypto activity. Circle, however, is gaining share in one of the most important growth lanes outside exchange trading.
The Bitcoin implication centers on liquidity, collateral, and who captures the next inflow
For Bitcoin, the stablecoin contest is not a side issue. Stablecoins fund exchange balances, back collateral positions, and give traders a dollar-linked unit that can move around the clock without leaving the crypto system.
When stablecoin supply grows, the market’s pool of deployable dollar liquidity tends to deepen. When one stablecoin gains more of that growth, the question becomes which venues and user groups will control the new liquidity.
Glassnode has described the Stablecoin Supply Ratio as a gauge of stablecoin-denominated buying power relative to Bitcoin supply, with lower readings implying greater potential purchasing power. That supports a practical point: stablecoins are one of the clearest ways to measure how much dollar liquidity is sitting inside crypto and how ready that liquidity may be to rotate into BTC.
If USDT remains the main store of offshore trading cash while USDC gains ground in regulated settlement and enterprise finance, Bitcoin liquidity could become more segmented over the next year. Offshore spot and derivatives venues may remain heavily USDT-centric.
Meanwhile, institutionally mediated Bitcoin activity could lean more toward USDC as banks, payment firms, and treasury desks choose the stablecoin that best fits compliance, reserve transparency, and settlement requirements.
That would not weaken Bitcoin. Tether would still matter most for the largest reservoir of crypto-native trading capital, and it could broaden the set of rails that feed Bitcoin demand.
Circle would matter more for the next tranche of regulated capital seeking a stablecoin bridge to digital assets without stepping outside traditional financial guardrails.
Standard Chartered has projected that the stablecoin market could reach $2 trillion by the end of 2028. From a base of roughly $315 billion today, that implies about $1.7 trillion of additional room for growth.
The key question is which issuer, reserve model, and regulatory framework will capture the next $1.7 trillion.
There are several plausible paths from here.
- USDT keeps the largest share of outstanding supply because its exchange and international distribution remain hard to replace, while USDC continues to gain in institutional payments and regulated settlement.
- Policy clarity and more bank integrations allow USDC’s lead in transaction velocity to translate into much bigger gains in outstanding supply.
- The market keeps assigning USDT the role of dominant crypto trading cash, and USDC’s gains remain meaningful but narrower, concentrated in regulated channels rather than across the full market.
The evidence today supports the first path more than the others. Tether is still too large, too embedded, and too useful across crypto’s global trading stack to call this an imminent overthrow.
Circle, though, has enough momentum in transactions, reserve design, and institutional integrations to argue that the next phase of stablecoin growth may not belong to the same issuer that dominated the last one.
Circle’s case also rests on recency, not just structure. USDC has hit a new market-cap high near $79 billion after roughly 8% monthly growth, while USDT has yet to reclaim the peak it reached in December 2025.
The broader takeaway for Bitcoin and the wider market is straightforward. USDT still owns the largest share of crypto’s cash inventory. USDC is making a stronger claim on crypto’s future cash plumbing.
If stablecoins are heading toward a multi-trillion-dollar market, the fight is no longer just about who is biggest now. It is about who captures the next wave of money, and which version of the dollar becomes the preferred bridge into Bitcoin, exchanges, payments, and on-chain finance.
The post Digital dollar power balance cracks as Circle’s growth spurt closes in on Tether’s dominance appeared first on CryptoSlate.
Washington is getting ready to potentially make life easier for the biggest US banks.
That can sound pretty abstract if you don't strip it down to the mechanics. Regulators decide how much capital banks must keep to absorb losses and how much liquidity they need if funding starts to disappear.
More capital and more liquidity make banks sturdier, though they also limit how much money banks can lend, trade, or return to shareholders. Less of both gives banks more room to move while leaving a thinner cushion when conditions turn.
That tradeoff is now back at the center of US bank policy. On March 12, Federal Reserve Vice Chair for Supervision Michelle Bowman said regulators are preparing a softer rewrite of the long-disputed Basel III endgame rules, the post-2008 capital package Wall Street has spent years trying to weaken.
The new version could leave large-bank capital requirements roughly flat or slightly lower than current levels once related changes are included, and could free up more than $175 billion in excess capital across the industry. Surcharges for the largest global banks may also fall by about 10%.
That is a sharp turn from where the debate stood less than three years ago.
The earlier draft, pushed under Bowman's predecessor, Michael Barr, in 2023, would have raised capital requirements at the biggest banks by about 19%. Banks argued that the proposal would make credit more expensive, reduce market-making capacity, and push activity out of the regulated system.
Their critics argued the opposite: years of easy money, concentrated asset exposures, and repeated stress episodes had made thicker buffers necessary. The new draft lands much closer to the banks' side of that argument.

The contrast is especially striking for Bitcoin: while Washington appears ready to give large banks more flexibility on capital and liquidity, direct crypto exposure can still attract far harsher treatment, suggesting regulators remain more comfortable backstopping traditional balance-sheet risk than normalizing Bitcoin on bank books.
The real policy turn is bigger than capital
On its own, that would already be a major banking story. What gives it wider reach is the second piece moving alongside it: liquidity.
Earlier this month, Treasury officials said they were taking a fresh look at liquidity rules and floated an idea that would give banks some regulatory credit for collateral they have already prepositioned at the Federal Reserve's discount window.
In plain terms, regulators may start treating part of a bank's ability to borrow emergency cash as usable liquidity. Treasury described that borrowing capacity as “real, monetizable liquidity.”
That means banks may no longer need to carry quite as much dead weight if they can show they already have assets lined up at the Fed and can turn them into cash quickly. The system, in other words, is being redesigned around a more direct role for the central bank backstop.
For years, regulators tried to build a framework that would make banks self-reliant in a panic. They were supposed to hold enough liquid assets to survive a run and treat the Fed's discount window as an emergency tool of last resort.
But in practice, banks have long avoided the window because using it is seen as a clear sign of distress. Treasury is now openly saying that this stigma is a problem and that the rules should better reflect the reality that the discount window exists to be used.
That lands differently only three years after the regional bank failures of 2023.
Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank, and First Republic collapsed because confidence vanished fast, depositors moved faster, and liquidity that looked available in theory proved much harder to mobilize in real time.
The Fed's own review of SVB said the bank had serious weaknesses in liquidity risk management and that supervisors failed to fully grasp how exposed it had become as it expanded. The official answer then was straightforward: banks needed better oversight, better preparation, and stronger resilience.
The 2026 rewrite says the system also needs lighter capital requirements, a less punitive treatment of discount-window readiness, and fewer constraints on the biggest institutions.
More room for banks, less friction in the system
If the new framework goes through, large banks would have more room to extend credit, increase trading capacity, repurchase shares, and support deal activity.
Supporters say that's exactly the point. Bowman argued that excessive capital requirements carry real economic costs and can interfere with banks' basic job of supplying credit to the broader economy. Industry groups made the same case, saying the revised plan would align requirements more closely with actual risk.
The other side of that trade is just as clear.
Capital rules are a shock absorber, and liquidity rules are a form of brake. Ease both at the same time and banks get more freedom while the system carries less built-in friction. It moves the official balance away from maximum safety and toward efficiency, credit creation, and smoother access to Fed funding.
However, the Fed's biggest problem now is timing.
Senator Elizabeth Warren warned against weaker capital standards while geopolitical and credit risks are already climbing. While her objection is political, it still nails the contradiction at the center of the debate.
After SVB, Washington said bank resilience had to come first. Now, with growth fears, market volatility, and funding sensitivity back in view, Washington is preparing to give the largest banks more room to breathe.
The consequences are simple.
This is a decision about how much slack to keep in the financial system before the next stress event arrives. A stricter framework will force banks to carry more idle protection. A softer one will accept a little more vulnerability in exchange for more lending, more market activity, and less drag on profitability.
Bitcoin's critique of the banking system has always been strongest when policymakers expand the role of emergency support while presenting the overall structure as stable and self-contained.
The discount window isn't a side detail in that story, but part of the infrastructure that keeps confidence from breaking all at once.
When Treasury starts arguing that prepositioned Fed collateral should count more directly in bank liquidity rules, it's acknowledging that the system still depends on central-bank rescue architecture even in periods sold as normal.
A crisis isn't near, but Washington is set on rewriting the post-SVB rulebook. This time, it wants to base it on a very pragmatic assumption, which is that when the next panic hits, the biggest banks need to have more flexibility and the Fed's backstop needs to be easier to use without hesitation.
It's certainly a much-needed relief for Wall Street.
For everyone else, though, it's a reminder that the banking system is still being tuned around the same old problem: private risk-taking works best when public liquidity is always close at hand.
The post Washington prepares $175B break for big banks — weakening protections against financial crisis appeared first on CryptoSlate.
On Mar. 13, the US economy delivered a data dump that landed somewhere between uncomfortable and alarming.
The GDP for the 2025 fourth quarter was revised down to 0.7% from an initial estimate of 1.4%, following 4.4% growth in the third quarter.
January core PCE rose 3.1% year over year, with a 0.4% monthly increase. January durable-goods orders were virtually unchanged, while core capital goods orders came in flat, with shipments down 0.1%. Real consumer spending edged up just 0.1%.
These numbers were delayed by last year's 43-day shutdown and hit the market after the Feb. 28 start of the US-Israeli war on Iran. Oil spiked to $119.50 this week before easing back to near $100. US gasoline prices are up 20% to $3.58 a gallon since the war began.
The Fed meets Mar. 17-18, and futures markets have scaled back expected 2026 rate cuts to about a one-quarter-point move by December, down from two before the conflict.
Bitcoin, meanwhile, has been showing early signs of stabilization. Since Mar. 11, ETF inflows have returned, spot demand has begun to recover, funding has turned negative, and options volatility has eased.
Into the weekend, BTC trades around $70,600 as of press time after hitting $74,000 intraday on Mar. 13. US spot Bitcoin ETFs took in a net $583 million from Mar. 9 through Mar. 12, according to Farside Investors data, following a $348.9 million outflow on Mar. 6.
However, the reality is that Bitcoin's fragile rebound is running straight into the worst possible macro mix for risk assets: slower growth, sticky inflation, and a Federal Reserve with fewer clean options.
The economy was already softening
The GDP revision tells a deeper story than the headline number suggests.
The downward adjustment came from weaker exports, consumer spending, government spending, and investment.
Real final sales to private domestic purchasers, a cleaner gauge of underlying domestic demand, slowed to 1.9% from an initial estimate of 2.4% and from 2.9% in the third quarter.
That means the economy entered the Iranian oil shock on a shakier footing than the original fourth quarter release implied. Nominal consumer spending rose 0.4% in January, but real spending barely budged.
| Indicator | Latest reading | Prior / comparison | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q4 2025 GDP | 0.7% | 1.4% initial estimate / 4.4% in Q3 | Growth slowed sharply |
| Real final sales to private domestic purchasers | 1.9% | 2.4% initial / 2.9% in Q3 | Cleaner read on domestic demand |
| Core PCE inflation | 3.1% YoY | Fed target: 2.0% | Underlying inflation still sticky |
| Real consumer spending | 0.1% MoM | Nominal spending: 0.4% | Consumers are spending, but barely in real terms |
| Core capital goods orders | Flat | Shipments: -0.1% | Business investment lost momentum |
Business equipment demand lost momentum, with core capital goods orders flat and shipments down.
The inflation side adds pressure. January headline PCE came in at 2.8% year over year, but core PCE rose to 3.1%, with a 0.4% monthly increase.
That puts the Fed's most closely watched inflation measure well above the 2% target. The central bank's current target range is 3.50% to 3.75%, unchanged since January.
The twist that makes this more urgent is that all of these numbers predate the energy shock.
The February CPI and the delayed January PCE period came before the strikes at the end of February, while the war-driven oil spike only hit afterward.
The backward-looking data already looked uncomfortable before the energy shock fully feeds through.
Economists are now warning that higher energy costs could worsen the trade-off between growth and inflation.
Goldman Sachs said a temporary move to $100 oil could shave 0.4% off global growth and add 0.7% to global headline inflation in its upside scenario.
Reuters reported that economists see March consumer prices potentially rising as much as 1%.
Bitcoin's fragile internals face a real test
The Federal Reserve meets Mar. 17-18, and markets widely expect the central bank to hold rates steady.
The bigger test is what the Fed Chair Jerome Powell says about the macro crosscurrents.
Rate-cut expectations have already been pushed back amid the war, which complicates the inflation outlook.
The classic bad menu is now in front of the Fed: slower growth, sticky prices, and an energy shock that could make both worse. If Powell leans more heavily on inflation patience than on downside-growth worries, risk assets face a tougher environment.
If he acknowledges greater energy-related uncertainty while maintaining a cautious tone, the market remains stuck in a holding pattern.
The problem for Bitcoin is that neither path offers much support. A hawkish hold reinforces “higher for longer” rates while also signaling slower growth. A dovish-but-cautious hold keeps the macro overhang in place without delivering relief.
Bitcoin has better near-term internals than the macro backdrop warrants, making the next few weeks more interesting. ETF flows turned positive again after a brief period of outflows.
Funding has turned negative rather than euphoric, which removes some froth from the market.
Options volatility has eased, and Glassnode noted growing upside interest around $75,000 alongside a main demand zone at $60,000 to $69,000.
The market is stabilizing, though Glassnode described conditions as fragile, with spot demand beginning to recover rather than fully recovered. The question is whether that stabilization can hold together while the Fed and oil backdrop deteriorate.
| Scenario | Macro trigger | Fed tone | Likely BTC implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bull | Oil retreats from spike | Shock treated as temporary | BTC can retest $75,000 |
| Base / holding pattern | Oil stays elevated but stable | Cautious hold, uncertainty emphasized | BTC stays range-bound |
| Bear | Oil near $100, inflation fears harden | “Higher for longer” reinforced | BTC vulnerable to $60,000–$69,000 demand zone |
| Black swan | Prolonged Hormuz disruption | Policy trap narrative | BTC trades like a stressed risk asset |
If oil keeps retreating from this week's spike and the Fed treats the energy shock as serious but temporary, Bitcoin's next clean test is the $75,000 area.
Goldman still expects Brent to drift back toward the low $70s later this year in its central view. Continuing ETF inflows would support a move higher.
If oil stays near $100 and inflation fears harden, Bitcoin becomes vulnerable to a retest of the $60,000 to $69,000 demand zone.
The market would be pricing “higher for longer” rates and slower growth simultaneously, which is a difficult combination for any risk asset.
The black swan scenario is a prolonged disruption of the Hormuz disruption that shifts the narrative from “temporary energy hit” to “policy trap.” In that case, Bitcoin behaves as a stressed risk asset.
Why does this extend beyond crypto
This is the classic bad menu for anyone with stocks, retirement accounts, mortgages, or exposure to risk assets.
| For mainstream investors | For crypto investors |
|---|---|
| Slower growth threatens stocks and earnings expectations | Bitcoin is being tested by worsening macro, not just crypto-specific sentiment |
| Sticky inflation keeps pressure on borrowing costs and mortgages | “Higher for longer” rates are a tough backdrop for fragile rebounds |
| Higher gasoline and energy costs hit households directly | ETF inflows and better internals help, but may not offset macro stress |
| The Fed has less room to cushion a slowdown | BTC must prove stabilization can survive a macro shock |
The economy looked softer than advertised even before the oil shock, and now the Fed has less room to help if growth worsens.
For crypto holders, what is worth watching is Bitcoin being asked to prove it can hold together while ETF demand improves, but the Fed and oil backdrop deteriorate.
The market is not entering this test in full-blown mania mode, which is actually the stronger setup. Funding is negative, volatility has eased, and flows have stabilized.
The challenge is that macro conditions are worsening faster than Bitcoin's internal repair is progressing. The economy was already losing momentum before the oil shock arrived.
Business investment started the first quarter weakly. Consumer spending barely grew in real terms. Core inflation is sticky, and gasoline prices are moving higher in real time.
The Fed meets next week, and Powell will have to navigate a deteriorating growth-inflation mix with limited tools. Markets have already scaled back rate-cut expectations.
If the energy shock persists, the policy choices get harder.
Bitcoin's stabilization is real, but the worst possible macro environment is testing it for a fragile rebound.
The post Bitcoin price faces a crucial weekend test as US growth collapses to 0.7% while inflation stays stubborn appeared first on CryptoSlate.
Binance suing the Wall Street Journal is not a new kind of signal, as the exchange has fought what it considered hostile coverage before.
However, this time the market may read the move differently.
In earlier cycles, a Binance-versus-media clash fit neatly into a larger story of regulatory danger. Now, after a softer US enforcement turn and deeper overlap with President Donald Trump-linked crypto networks, the same kind of pushback may be read less as panic and more as confidence.
On Mar. 11, Binance sued the Wall Street Journal and Dow Jones over a Feb. 23 report tied to an alleged Iran-related internal investigation, saying the story made false and defamatory claims about how Binance handled roughly $1 billion in transfers allegedly linked to Iran-backed groups.
The suit says the Journal ignored corrections and published at least 11 false statements.
That sounds familiar because it is. Reuters previously reported that Binance sued Forbes over its 2020 “Tai Chi” article and later dropped the case.
Additionally, Binance founder Changpeng Zhao (CZ) personally sued Bloomberg Businessweek's Hong Kong publishing partner, Modern Media, in 2022 over a “Ponzi scheme” headline.

The novelty in the WSJ fight lies in the backdrop against which the tactic is being used.
In 2020 and 2022, a Binance-versus-media clash slotted naturally into a broader narrative of regulatory danger. In 2026, the same move followed the SEC's dismissal of its civil case with prejudice, after Trump-linked World Liberty's USD1 was reportedly used in MGX's $2 billion Binance investment, and after Trump pardoned CZ.
Same tactic, different setting
Binance may be facing a friendlier US climate, but the Iran-related scrutiny and ongoing litigation show the fear premium is shrinking, not gone.
Senator Richard Blumenthal opened a preliminary inquiry in February 2026 after reporting on alleged sanctions exposure related to Iran and Russia.
Reports also noted that, in late February 2026, a federal judge refused Binance's attempt to force certain customer-loss claims into arbitration.
And on Mar. 6, Reuters reported that Binance and Zhao had won dismissal of a lawsuit by victims of 64 attacks, but the judge allowed the plaintiffs to amend the complaint.
In February 2025, Binance and the SEC jointly requested a pause in the agency's case as Trump's crypto policy took shape. In May 2025, the SEC dismissed the case with prejudice and said the move was appropriate “in the exercise of its discretion and as a policy matter,” not because the merits had been fully vindicated.
Also in May, Trump-linked USD1 would be allegedly used to close MGX's $2 billion Binance investment. In October 2025, Trump pardoned CZ.
The WSJ lawsuit now sits atop that sequence.
| Event | What happened | Why it changed the Binance risk read |
|---|---|---|
| Feb. 2025 | Binance and the SEC jointly sought a pause in the agency’s case | Suggested a softer US policy posture might be emerging |
| May 2025 | The SEC dismissed its civil case against Binance with prejudice | Lowered the perceived civil-enforcement overhang |
| May 2025 | Trump-linked USD1 was reportedly used in MGX’s $2 billion Binance investment | Tied Binance more closely to Trump-adjacent crypto networks |
| Oct. 2025 | Trump pardoned CZ | Reinforced the idea that Washington risk may be lower than before |
| Feb. 2026 | Sen. Richard Blumenthal opened a preliminary inquiry | Showed the fear premium is shrinking, not gone |
| Late Feb. 2026 | A federal judge refused Binance’s attempt to force certain customer-loss claims into arbitration | Confirmed that legal vulnerability remains real |
| Mar. 6, 2026 | Binance and Zhao won dismissal of a lawsuit by victims of 64 attacks, but plaintiffs were allowed to amend | Not a full all-clear; litigation risk still lingers |
| Mar. 11, 2026 | Binance sued WSJ / Dow Jones | The same old tactic now lands inside a different, more politically favorable backdrop |
The clean investor takeaway is that the fear premium around Binance may be shrinking. For years, damaging headlines about Binance were often read as possible preludes to a fresh regulatory shock.
If Washington now looks less hostile, then the same headlines may no longer trigger the same fear response. That matters for competitor positioning, headline sensitivity, and how the market prices Binance's legal noise.
The lawsuit itself fits that interpretation. A company that still sees itself as maximally exposed tends to play defense. Binance instead escalated into open legal combat with one of the world's most influential financial publications.
Despite not proving insulation, it suggests Binance believes the downside of fighting back is lower than it used to be.
The political read layers onto scale
The political angle should not swallow Binance's actual business strength.
Binance remains the dominant centralized exchange by spot volume: CoinGecko said it held 38.3% of total spot volume in December 2025 and 39.2% of top-10 CEX spot volume for full-year 2025.
In February 2026, Binance served about 300 million users and held roughly $44 billion in Bitcoin in customer wallets.
A friendlier political read may be to layer on scale and liquidity rather than replace them.
The visible conflict is between Binance and the WSJ, while the deeper conflict is between two narratives about the company. The old narrative cast Binance as a permanently vulnerable regulatory target.
The newer one says the exchange may now be operating in a friendlier US climate, where scale, global relevance, and Trump-adjacent crypto overlap reduce the market impact of hostile coverage.
The market may be seeing the same playbook play out in a friendlier US regime.
Forward scenarios
The bull case for this new Binance clash is that the market increasingly concludes that the old US crackdown template no longer lands the same way on Binance.
The SEC dismissal, the pardon, and the reportedly Trump-linked USD1/MGX overlap fit into a broader narrative that Binance is less liable than before.
In that case, the WSJ suit looks less like defensiveness and more like incumbent confidence.
The bear case is that investors overread the friendliness. The Iran-related controversy, congressional scrutiny, or civil litigation reminds the market that Binance still has real legal vulnerability.
In that scenario, the WSJ lawsuit gets reinterpreted as overreach, and the supposed shrinkage in fear premium reverses.
The black swan is that a formal US sanctions or national security action emerges from the Iran-related reporting. Then the whole “friendlier backdrop” thesis flips from support to liability because the market would suddenly relearn that political narratives do not neutralize hard enforcement when national security is at stake.
| Scenario | What investors assume | How the WSJ lawsuit gets read | Market consequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bull case | The old US crackdown template no longer lands the same way on Binance | The lawsuit reads as confidence and incumbent strength | Binance’s fear premium shrinks further |
| Base case | Washington is friendlier, but Binance is still exposed to some real legal risk | The lawsuit reads as aggressive but manageable | Headline panic weakens, but some enforcement discount remains |
| Bear case | Investors overread the friendliness and underestimate remaining legal vulnerability | The lawsuit reads as overreach | Binance’s enforcement discount widens again |
| Black swan | Iran-related reporting leads to formal US sanctions or national-security action | The lawsuit looks reckless in hindsight | The political-insulation thesis breaks and risk gets repriced sharply |
The investor question is “Why might the same move create less fear this time?”
For years, the “Binance discount” was simple: any damaging headline could be read as the prelude to another major enforcement blow.
That transmission mechanism may be weakening. If investors increasingly think the old crackdown playbook no longer lands the same way, then bad headlines lose some of their panic power, Binance's enforcement discount shrinks, and competitors that benefited from “Binance fear” lose some of their relative advantage.
Binance suing the press is old behavior. The market may be reading it through a softer US policy backdrop as the new part.
What makes this WSJ clash worth watching is whether the same old tactic now hits investors through a different lens. One where Washington looks less like a threat and more like uncertain terrain that Binance feels confident enough to navigate aggressively.
The post Why Binance suddenly isn’t afraid of negative press anymore appeared first on CryptoSlate.
A crypto trader lost over $50 million in Aave-wrapped USDT on March 12 after sending a single large order through the DeFi lending protocol's swap interface and clearing a slippage warning on a mobile device.
Data from Etherscan shows the wallet swapped $50.43 million aEthUSDT for 327.24 aEthAAVE through CoW Protocol in Ethereum block 24,643,151.
At the current AAVE price of $111.52, the returned tokens were worth roughly $36,100, leaving an implied loss of about $49.96 million relative to the original order size.
The trade drew immediate attention across crypto markets because of its scale and because it moved through one of decentralized finance’s largest venues. Aave is the largest DeFi lending protocol with over $1 trillion in total cumulative lending.
Following the incident, Aave revealed plans to contact the affected user and return about $600,000 in fees collected from the transaction. CoW Protocol said it would also refund any fees sent to CoW DAO.
Who is the victim?
Blockchain analytics platform Lookonchain said the wallet behind the swap may belong to Garrett Jin, a popular crypto trader known as the BitcoinOG1011short.
Lookonchain said on-chain tracing identified 13 wallets that may belong to Jin. It said those wallets received USDC or USDT from Binance on Feb. 16 and Feb. 20, then became active again on Thursday and moved funds to two new wallets.
One of those wallets, Lookonchain said, shared the same Binance deposit address as Garrett Jin.
The claim drew significant attention because Jin has already been linked to other large, closely watched crypto trades.
Last October, online sleuths tied him to a $735 million short position on Bitcoin opened through Hyperliquid shortly before President Donald Trump threatened additional tariffs on China.
The trade, which made up to $200 million in profit, later fueled speculation about advance knowledge because it arrived just before a broader market selloff.
However, Jin rejected that narrative, saying the capital belongs to clients. He added that his team runs nodes and provides in-house insights, and that he has no connection to the Trump family.
As of press time, Jin had yet to confirm any link to the $50 milion loss.
Ethereum middlemen share the windfall
While the trader absorbed the loss, other participants in Ethereum’s execution chain captured the spread released by the order.
Emmet Gallic, an analyst at Arkham Intelligence, said a maximal extractable value, or MEV, bot arbitraged the transaction across Uniswap and SushiSwap pools.
In Ethereum markets, MEV refers to profits captured by automated traders when they react to pricing gaps created during block execution.
Gallic said the bot paid Titan Builder 16,927 ETH, worth about $34.8 million. Titan Builder then paid 568 ETH, or about $1.2 million, to the Lido validator associated with the block proposal and kept about 16,359 ETH, or roughly $33.6 million. The bot operator was left with about $10 million in gains.

As a result, Titan Builder generated the highest revenue among crypto platforms in the last 24 hours, according to DeFiLlama data.
Aave and CoW say the user was warned about the transaction
Meanwhile, the DeFi protocols Aave and CoW have both defended their platforms in this loss, stating that the user received a clear warning notice before the order was executed.
Aave founder Stani Kulechov explained that the user had manually overridden a warning signal that flagged unusually high slippage and then proceeded with the swap on mobile.
According to him:
“The transaction could not be moved forward without the user explicitly accepting the risk through the confirmation checkbox.”
He described the result as “clearly far from optimal” and said Aave’s team would review stronger safeguards around similar trades.
CoW Protocol gave a similar account, while explaining that:
“There’s no indication of a protocol exploit or otherwise malicious behavior. The transaction executed according to the parameters of the signed order.”
CoW also said available public and private liquidity sources could not support a reasonable fill for an order of that size.
Their explanation placed the focus on execution conditions rather than software failure. The route searched for available liquidity, found a path, and carried the order across venues that repriced as the size moved through them.
The warning flow recorded the user’s approval before the trade reached the market.
Improving DeFi user experience
As a result, the episode has brought renewed attention to how DeFi interfaces handle oversized orders.
Suhail Kakar, a developer relations executive at Polymarket, said the incident showed a gap in DeFi user protections rather than a failure of the underlying contracts.
He said Aave and CoW Swap executed the trade as designed, but warned that a mobile confirmation flow should not stand between a user and a $49.9 million loss due to slippage.
Kakar added that wallets and frontends should more clearly show the expected dollar loss and introduce stronger controls for oversized orders, including mechanisms that split large trades into smaller transactions.
In response, Kulechov said Aave would implement stronger safeguards to prevent a recurrence, while CoW said the trade showed the need to keep improving the DeFi user experience.
According to CoW:
“Preventing users from making trades removes choice and can lead to terrible outcomes in some situations (e.g. a market crash). That said, trades like these show that DeFi UX still isn’t where it needs to be to protect all users. As a team, we are now reviewing how we balance strong safeguards with preserving user autonomy.”
The post Miss this warning and you too could lose 99.9% in one swap while Ethereum bots walk away with the rest appeared first on CryptoSlate.
Cryptoticker
The institutional appetite for digital assets is showing renewed vigor as BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) recorded a substantial purchase of approximately $147.7 million worth of Bitcoin. This latest acquisition is not an isolated event; it marks the third consecutive week of net inflows for the world’s largest spot Bitcoin ETF, signaling a decisive shift in market sentiment.
Institutional Confidence Returns to BTC
After a period of stagnant price action and cooling interest in early 2026, the tide appears to be turning. The consistent inflow into IBIT suggests that institutional allocators are viewing current price levels as a strategic entry point. This "three-peat" of weekly gains provides a necessary cushion for the Bitcoin price, which has faced significant volatility in recent months.
Market Impact and "Giga-Bullish" Signals
The magnitude of these inflows often serves as a leading indicator for broader market movements. When a behemoth like BlackRock consistently accumulates, it reduces the available liquid supply on exchanges, creating a "supply shock" environment.
- Sustained Momentum: Three weeks of inflows suggest this is a trend, not a "dead cat bounce."
- Liquidity Concentration: BlackRock now manages a significant portion of the total crypto news cycle, often dictating the daily momentum of the entire asset class.
- Wider Adoption: This streak coincides with BlackRock's expansion into other products, such as their recently launched staked Ethereum ETF (ETHB), further cementing their dominance in the digital asset space.
Strategic Outlook for Traders
While the "giga-bullish" narrative is gaining steam, traders should remain aware of macroeconomic headwinds that could impact the pace of these inflows. However, for now, the data is clear: BlackRock is buying, and the institutional gate is wide open.
The stablecoin sector has officially crossed a historic threshold, reaching a total market capitalization of $320 billion as of March 2026. This vertical climb represents more than a mere recovery from previous cycles; it marks the "industrialization" of digital dollars. Unlike the retail-driven spikes of the past, the current momentum is fueled by multi-billion dollar inflows from traditional finance (TradFi) giants and the implementation of the GENIUS Act in the United States.
What is Driving the Stablecoin Surge?
The primary driver behind the $320 billion market cap is the rapid transition of stablecoins from speculative trading tools to global payment infrastructure. In January 2026 alone, stablecoin networks moved over $10 trillion in transaction volume—a figure that now rivals legacy settlement systems like Visa. This "vertical" adoption is led by institutional demand for 24/7 settlement and the legislative "green light" provided by federal regulators.
Market Composition: The Rise of Regulated Giants
While Tether (USDT) remains the liquidity heavyweight with a market cap of approximately $184 billion, the narrative in 2026 has shifted toward compliant, onshore alternatives.
- Circle (USDC): Has seen explosive growth, reaching $78 billion, outperforming the broader sector in monthly growth due to its status as the "compliance-first" choice for U.S. institutions.
- BlackRock BUIDL: The tokenized liquidity fund has surged 36% recently, hitting $2.46 billion, proving that yield-bearing institutional "stable-assets" are a core growth pillar.
- USAT: Tether’s newly launched, U.S.-regulated stablecoin is already challenging the status quo, aiming to capture the institutional market governed by the GENIUS Act.
The Impact of the GENIUS Act
The Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins (GENIUS) Act, signed into law in mid-2025, has redefined the market. By mandating 1:1 liquid reserves and federal oversight, the act has effectively de-risked stablecoins for the 1,600+ local banks now plugging into these rails via providers like Jack Henry.
This regulatory framework has bifurcated the market:
- Onshore Regulated Rails: Used for B2B payments, payroll, and corporate treasury.
- Offshore Liquidity Routes: Still dominated by USDT for global retail and high-frequency trading.
Institutional "Vertical" Adoption: Beyond Trading
The current growth is "vertical" because it is expanding upward into the highest levels of the financial stack. BNY Mellon now acts as a custodian for major tokenized funds, and Aon has begun settling insurance payments in USDC.
Conclusion: The Path to $1 Trillion
Market analysts, including those from the European Central Bank, suggest that if current trends hold, the stablecoin market cap could hit $1 trillion by 2027. As stablecoins continue to eat into traditional bank deposits, they are becoming a systemically important part of the global economy—no longer a "crypto niche," but the very plumbing of modern finance.
The geopolitical landscape shifted violently two weeks ago with the outbreak of a military conflict between the US and Iran. While traditional markets are reeling from the shock, the digital asset class is showing unexpected resilience. Since the start of hostilities, an estimated $2.4 trillion has been erased from the US stock market as investors flee from risk-heavy equities.
In a striking divergence, the crypto market cap has added nearly $250 billion during the same period. This decoupling suggests a shift in how institutional and retail investors perceive "digital gold" during times of extreme kinetic warfare. As oil prices surge and the Strait of Hormuz faces potential blockades, the 24/7 liquidity of $Bitcoin and other major assets is becoming a strategic refuge.
Is Crypto the New Safe Haven?
For years, analysts debated whether crypto would act as a "risk-on" asset or a "safe haven." The current conflict provides a real-time case study. While the S&P 500 and Nasdaq have suffered their worst two-week stretch since the 2025 tariff crisis, the crypto market has reclaimed significant ground.
- US Equities: $2.4 trillion in value wiped out (approx. -5.2% decline).
- Crypto Market: ~$250 billion added (over +5% increase).
Investors are navigating a world where traditional banking systems in conflict zones face outages, making borderless assets like $Ethereum and stablecoins more attractive for capital preservation and mobility.
Total Crypto Market Cap Analysis: The 5% Rebound
A closer look at the Total Crypto Market Cap (TOTAL) chart reveals a V-shaped recovery following the initial "panic sell" at the war's onset. After a brief dip to the $2.3 trillion level on February 28, the market surged back.

- Initial Shock: The first 48 hours saw massive liquidations as traders de-risked.
- The Rebound: As of March 14, 2026, the total market cap sits near $2.41 trillion, representing a recovery of over 5% from the local lows.
- Volume Spike: Trading volume has normalized at higher levels, indicating that the move is supported by actual accumulation rather than just a "dead cat bounce."
The Fear and Greed Index has moved from "Extreme Fear" (8/100) earlier this month toward a more neutral stance (29/100), as the market prices in a "war premium" and the potential for the Federal Reserve to pause rate hikes to maintain economic stability.
Why Stocks are Crashing While Crypto Rallies
The divergence comes down to inflationary fears and liquidity. The US-Iran war has pushed Brent crude oil prices toward $120 per barrel. In the stock market, high energy costs mean lower corporate margins and higher consumer prices, leading to a massive sell-off.
Conversely, the "debasement narrative" helps crypto. If the US government increases spending to fund military operations, the long-term outlook for the dollar weakens. Investors are preemptively moving into Bitcoin to hedge against this potential currency devaluation. Furthermore, according to reports from Morningstar, regional demand in the Middle East for non-sovereign assets has spiked as a means to move wealth across borders.
Why Are Gold and Silver Crashing While Bitcoin Is Rising?
Global markets are sending a confusing signal. Precious metals — traditionally considered safe haven assets during uncertainty — have suddenly dropped, while Bitcoin is moving in the opposite direction.
In the last few hours, silver fell sharply and gold also declined, wiping hundreds of billions of dollars from the metals market. At the same time, Bitcoin managed to reclaim the $73,000 level, even as geopolitical tensions and economic concerns dominate global headlines.
This unusual divergence is raising an important question: why are traditional safe havens falling while Bitcoin rises?

Gold and Silver See Sudden Sell-Off
Gold and silver markets experienced a sharp drop within a short period of time. According to market trackers, roughly $1 trillion in market value was wiped from the precious metals sector in just a few hours as both metals moved lower simultaneously.
Silver dropped significantly, falling below key support levels while gold also declined more than 2% during the sell-off.
Normally, geopolitical tensions or economic uncertainty push investors toward safe haven assets such as gold and silver. However, the recent move suggests something different may be happening in global markets.
One possible explanation is liquidity stress. When investors face uncertainty or margin pressure, they sometimes sell profitable assets — including metals — to raise cash.
Another factor may be profit-taking after strong rallies. Precious metals have surged in recent months, and some traders could be locking in gains during heightened volatility.
Economic Warning Signs Are Appearing
At the same time, new economic data is raising concerns about global growth.
Canada’s economy unexpectedly lost 83,900 jobs in February, one of the sharpest monthly declines seen in years. The surprising drop has triggered fears that economic momentum in North America could be slowing.
Weak employment data can affect global markets because it signals reduced consumer spending and potential economic contraction. When investors begin to worry about economic slowdowns, volatility often increases across multiple asset classes.
This kind of uncertainty can trigger sudden capital movements between markets.
Geopolitical Tensions Add More Pressure
Another key factor influencing markets is rising geopolitical tension.
Recent developments in the Middle East have increased concerns about energy supply disruptions. The Strait of Hormuz, one of the world’s most important oil shipping routes, remains a critical point of risk for global energy markets.
Around 20% of global oil supply passes through the Strait of Hormuz, meaning any disruption could send oil prices sharply higher and increase inflation pressures worldwide.
Such geopolitical risks usually push investors toward safe assets — but the current market behavior suggests investors may be repositioning capital differently this time.
Bitcoin Is Moving the Other Way
While metals fell, Bitcoin managed to reclaim the $73,000 level, showing resilience despite global uncertainty.

This raises an interesting possibility: Bitcoin may be starting to behave differently in the current macro environment.
For years, Bitcoin has been described as “digital gold.” During certain market events, investors view it as a hedge against monetary instability, inflation, or geopolitical shocks.
The recent move could reflect capital rotation, where investors move funds between asset classes depending on liquidity, volatility, and perceived opportunity.
In this case, some traders may see Bitcoin as offering higher upside potential compared with traditional safe havens.
A Strange Signal From Global Markets
The current market environment is unusual because several signals are happening at the same time:
- Gold and silver are falling
- Economic data is weakening
- Geopolitical tensions are rising
- Bitcoin is climbing
Such a combination suggests investors are still trying to determine where the safest and most profitable place for capital may be.
Whether Bitcoin continues to rise while metals struggle remains uncertain, but one thing is clear: global markets are entering a period of unusual volatility and shifting narratives.
Investors are currently transitioning from a state of "Extreme Fear" encountered earlier in the month toward a "Risk-On" appetite. This shift is primarily driven by the flagship cryptocurrency, Bitcoin ($BTC), which has successfully breached the $72,500 resistance and is now aggressively testing the psychological $73,000 milestone.
While the global macroeconomic landscape remains plagued by uncertainty—ranging from geopolitical tensions in the Middle East to shifting Federal Reserve policies—the "bears" are finally letting go. This decoupling from traditional equities suggests that cryptocurrencies are once again being viewed as a hedge against global instability. Within this bullish vortex, Cardano ($ADA) is positioning itself for a significant move.
Is ADA Price Heading to $0.40?
Yes, the current technical structure suggests that the Cardano price is preparing for a leg up toward the $0.40 mark. With Bitcoin providing the necessary market liquidity and sentiment tailwinds, ADA has managed to stabilize above its critical support levels. If the current buying pressure continues, $0.40 represents the first major resistance zone that could define the trend for Q2 2026.
The Macro Backdrop: Why Are Crypto Prices UP?
The broader market rally isn't just about price action; it’s about a fundamental shift in global liquidity. Several factors are contributing to this environment:
- Bitcoin Resilience: By trading near its all-time highs of $73,000, Bitcoin is acting as a "gravity well" for capital, pulling the rest of the altcoin market higher.
- Institutional Inflows: Spot Bitcoin ETFs have seen record inflows this week, totaling over $700 million, signaling that the "Smart Money" is betting on a continued expansion.
- Governance Milestones: For Cardano specifically, the implementation of the CIP-1694 governance model and the rollout of Plutus V3 have strengthened the network’s value proposition.
Cardano Price Analysis: Breaking Down the Chart
Analyzing the current ADA/USD price chart, we see a classic "Bottoming Out" formation. After a period of heavy consolidation between $0.25 and $0.28, ADA is finally showing signs of life.

Key Support and Resistance Levels
| Level Type | Price Point (USD) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Major Resistance | $0.40 | Target zone and psychological barrier. |
| Intermediate Resistance | $0.34 | The 50-day SMA and previous swing high. |
| Immediate Support | $0.26 | Current floor where accumulation is strongest. |
| Critical Support | $0.24 | The "must-hold" level to avoid a bearish reversal. |
Indicators and Momentum
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) for ADA has recently climbed out of the oversold territory and is currently hovering around 45-50. This indicates that there is plenty of "room to run" before the asset becomes overbought. Additionally, whale data indicates that large holders (wallets with 100M+ ADA) have accumulated nearly $35 million in tokens over the last 48 hours, suggesting they anticipate a breakout.
Cardano Price Prediction: The Path to $0.40 and Beyond
For the ADA price to reach $0.40, it must first reclaim the $0.313 level with high volume. This would invalidate the short-term bearish "head and shoulders" patterns seen on smaller timeframes.
- Phase 1 (The Breakout): A daily close above $0.30 would trigger a wave of FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out), likely pushing the price toward $0.34.
- Phase 2 (The Consolidation): Expect some resistance at the 200-day Moving Average (near $0.49), but a push to $0.40 is highly probable if Bitcoin holds above $71,000.
- Phase 3 (The Target): Once $0.40 is touched, Cardano would enter a new liquidity zone, potentially opening the doors for a move toward $0.54 by mid-2026.
According to data from Investing.com, the regulatory clarity provided by the upcoming "Clarity Act" in the US could be the final catalyst needed for this move.

What Should Investors Do?
While the outlook is bullish, traders should remain cautious of the "March Trap." High volatility means that "wick hunts"—where prices briefly dip to liquidate over-leveraged long positions—are common. It is essential to use proper risk management tools.
Summary of the Bullish Thesis
- Bitcoin (BTC) breaching $73,000 creates a "rising tide" for all alts.
- Whale accumulation suggests a market bottom has been formed for ADA.
- Technical Breakout: Cardano is eyeing a 40% gain from current levels to hit the $0.40 target.
Decrypt
Eddy Alexandre, who pleaded guilty to commodities fraud in 2023, is currently serving out a nine-year prison sentence
Twenty million Bitcoin mined. One million left. The miners who got us here might not be around for the finish.
Feds are looking to hear from victims after several games on Valve’s Steam platform were found to be distributing malicious software.
President Donald Trump's meme coin has surged by 35%, with top holders stacking Solana-based tokens to earn access to an exclusive event.
The company is taking a broad look at crypto-native firms that could generate interest on Wall Street.
U.Today - IT, AI and Fintech Daily News for You Today
A popular crypto analyst has revealed that Bitcoin still stands a chance at reclaiming $95,000 despite the short-term price dips if it is able to maintain a close above $73,726.
Pi Network, a token technically related to Stellar, crashed 30% in a matter of hours.
XRP sees continued demand despite the sudden price drop as payment activity on XRP Ledger surges by over 15% in 24 hours.
Bitcoin is currently trading above $70,000, with veteran trader Peter Brandt indicating further volatility could be in the cards.
XRP's price remains in the spotlight as indicators point to a bigger move brewing.
Blockonomi
TLDR:
- The 2Y SMA/2 is derived by halving the two-year simple moving average and has marked bottoms across BTC, ETH, BNB, and XRP.
- Solana, Dogecoin, and Cardano have already reached the 2Y SMA/2, placing them in historically deep discount territory this cycle.
- Chainlink tested the 2Y SMA/2 with precision and posted a bounce, reinforcing its role as a reliable long-term support zone.
- TRON remains nearly 50% above the 2Y SMA/2, standing out as one of the most resilient altcoins in the current bear market.
The 2Y SMA/2 is gaining renewed attention as crypto markets continue their downward trend. Derived by halving the two-year simple moving average, the indicator has consistently marked price bottoms across major cryptocurrencies.
Analyst Joao Wedson recently stated that all crypto bear markets eventually reach this level. His observation has sparked discussion among traders tracking long-term technical levels across the market.
A Simple Calculation With a Consistent Track Record
The two-year simple moving average is already a widely followed tool among crypto analysts globally. It smooths out short-term volatility by averaging price data over a 24-month period.
However, Wedson’s thread introduced a variation that carries even more historical weight. Dividing that average by two produces a level that has repeatedly aligned with major price bottoms.
This pattern has been observed across some of the largest cryptocurrencies by market cap. Bitcoin, Ethereum, BNB, and XRP have all respected the 2Y SMA/2 during past bear cycles.
Each of these assets eventually gravitated toward this level before staging meaningful recoveries. The consistency across different assets is what makes the indicator difficult to dismiss.
The calculation itself is straightforward, yet its market behavior is notable. A simple mathematical adjustment to a well-known moving average produces a reliable long-term floor.
This kind of simplicity often resonates with analysts who prefer tools grounded in price history. It requires no complex parameters, only a long enough dataset to derive meaningful readings.
Wedson’s post has drawn considerable attention within crypto analysis circles. The idea that bear markets follow a predictable path toward this level challenges the notion that bottoms are impossible to anticipate.
While no indicator offers certainty, the historical alignment between the 2Y SMA/2 and price floors is hard to overlook. Traders are now applying this framework across a broader set of altcoins.
How the 2Y SMA/2 Has Played Out Across Major Altcoins
Several altcoins have already reached the 2Y SMA/2 in the current bear cycle. Solana touched this level after spending nearly two years in sideways consolidation following a massive rally.
Dogecoin also arrived at the 2Y SMA/2, reflecting reduced memecoin interest compared to the 2021 cycle. Cardano has traded below it for weeks, hovering near its 2022 bear market lows.
Chainlink provided one of the cleaner technical reactions to this level recently. It tested the 2Y SMA/2 with precision and posted a modest bounce shortly after contact.
This type of price behavior reinforces the idea that the indicator functions as a meaningful support zone. Such reactions are consistent with how long-term moving averages have historically behaved.
Bitcoin Cash is currently sitting directly on the 2Y SMA, one step above the 2Y SMA/2. Whether it drops further to the lower level remains an open question for analysts.
Wedson suggested patience before drawing conclusions on BCH’s next directional move. The asset’s behavior over coming weeks may offer clearer signals.
TRON stands out as an exception in the current environment. It remains well above both the 2Y SMA and the 2Y SMA/2, requiring roughly a 50% decline to reach either level.
Its resilience sets it apart from the broader altcoin market. Hyperliquid, despite being a newer project, is also showing relative strength and gaining traction while others consolidate.
Why Traders Are Watching the 2Y SMA/2 Closely Right Now
The broader crypto market is in a phase where long-term indicators carry more relevance than short-term signals. Many assets are trading near multi-year lows, making historical support levels increasingly important.
The 2Y SMA/2 offers a reference point grounded in two full years of price data. That depth gives it more credibility than shorter-term moving averages in bear market analysis.
Wedson’s observation is not based on a single asset or isolated event. The pattern has repeated across BTC, ETH, and a growing list of altcoins over multiple market cycles.
Each confirmation adds to the indicator’s standing as a reliable long-term floor. Analysts are now expanding its application to assess where other assets stand relative to this benchmark.
For traders with longer time horizons, assets trading at or below the 2Y SMA/2 represent zones of historical interest. The indicator does not predict the timing of a recovery, but it identifies price regions that have preceded past rebounds.
Understanding where an asset sits relative to this level provides useful context. It helps separate assets at deep discount from those still carrying elevated downside risk.
The current cycle is testing the 2Y SMA/2 across more assets simultaneously than in previous bear markets. That broad convergence reflects the depth of the current correction.
As more cryptocurrencies reach this level, the indicator’s relevance grows across the market. Wedson’s framework gives analysts a consistent lens through which to measure how far the bear market has progressed.
The post 2Y SMA/2: The Crypto Bear Market Indicator That Has Called Every Major Price Bottom appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR:
- IOTA’s code reveals a three-tier securitization model mirroring traditional structured finance architecture.
- The infrastructure could support invoice factoring, SME lending, and energy project financing on-chain.
- Analysts link the testing to SALUS and ADAPT platforms operating within the AfCFTA trade framework.
- No IOTA Foundation statement confirms the purpose, but the architecture suits digital capital markets.
IOTA is currently testing a full securitization infrastructure on its blockchain, based on early code analysis. The architecture mirrors traditional structured finance models, dividing pooled assets into senior, mezzanine, and junior tranches.
This points toward a broader financial layer being constructed on the IOTA network. Community observers are connecting this work to platforms like SALUS, ADAPT, and TWIN. All three platforms operate within the African Continental Free Trade Area framework.
IOTA Code Points to a Foundational Structured Finance Layer
Securitization involves pooling real assets, like loans or invoices, and converting them into tradeable instruments. On IOTA, the code being tested applies this same principle across the network.
This structure points to a foundational layer for managing and structuring real-world assets on-chain.
The architecture reflects the three-tier model widely used in traditional structured finance. Senior tranches carry the lowest risk and hold first priority on repayment.
Mezzanine tranches occupy the middle ground, balancing risk and return. Junior tranches carry the highest risk but offer the greatest potential return.
Community analyst Salima flagged this on X, noting the architecture fits platforms like SALUS and ADAPT. She pointed out that the code does not appear to be a standalone product.
Rather, it resembles the base layer for managing digital real-world assets at scale. Any direct link to AfCFTA trade platforms remains unconfirmed at this stage.
What stands out is that this process could run entirely on IOTA without external financial rails. No third-party intermediaries or legacy systems would be required.
Portfolios of real-world assets could become programmable digital financial structures on-chain. Investors could then participate based on their individual risk profiles.
Trade Finance to Capital Markets: IOTA’s Potential Use Cases
The infrastructure on IOTA could support several practical financial applications. Invoice factoring and trade finance are among the most immediate potential use cases.
SME lending and productive financing also fit within this securitization model. Equipment leasing and energy projects are additional sectors where this architecture could apply.
Digital capital markets for real-world assets represent a wider area of interest. Tokenized portfolios could open participation to a broader global investor base.
This removes the geographic barriers that traditionally limit access to structured finance. IOTA’s feeless and scalable design makes it technically suited for this type of infrastructure.
The timing of these tests aligns with growing global interest in real-world asset tokenization. Traditional finance is increasingly exploring blockchain alternatives to legacy securitization models.
If IOTA’s architecture develops further, it could serve as a foundational layer for this shift. No official statement has come from the IOTA Foundation as of this writing.
As the code evolves, observers are watching for further technical developments and announcements. The current architecture does not confirm any specific platform or official partnership.
What is clear is that IOTA is building technical groundwork for real-world asset finance. The full scope and intent of this infrastructure is yet to be publicly confirmed.
The post IOTA Tests Securitization Infrastructure That Could Reshape Real-World Asset Finance on Blockchain appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR:
- Over 240,000 ETH worth approximately $480M has been accumulated by whales since early March 2025.
- BlackRock’s ETHB ETF on Nasdaq lets institutions earn yield by staking 70–95% of their ETH holdings.
- Rising Ethereum active addresses during a price decline mirror historical accumulation patterns seen since 2022.
- Shrinking ETH exchange supply combined with whale buying could trigger a supply squeeze in the coming weeks.
ETH whale accumulation has reached unprecedented levels as BlackRock’s iShares Staked Ethereum Trust ETF begins trading on Nasdaq.
Over 240,000 ETH, worth approximately $480 million, has been stacked since early March. The price of ETH remains range-bound between $1,900 and $2,150.
Network activity data also points to growing bullish momentum. Active addresses on the Ethereum network have risen sharply.
This signals that accumulation is actively driving on-chain engagement amid the current price stagnation.
Whales and Institutions Drive ETH Demand
Crypto analyst CryptosRus flagged the trend on social media, noting that whales are stacking ETH at a remarkable rate.
The accumulation of over 240,000 ETH since early March has drawn broad market attention. Despite this sustained buying pressure, the ETH price has not yet broken out of its current range.
BlackRock’s iShares Staked Ethereum Trust ETF now trades under the ticker ETHB on Nasdaq. This product has introduced a fresh layer of institutional demand into the ETH market.
The ETF allows institutions to gain direct exposure to ETH while staking between 70% and 95% of holdings for yield. It gives institutional participants both price exposure and a passive income stream at once.
In the early days of trading, approximately $2.2 million flowed into the ETF. While that figure remains modest, the product’s structure could attract larger capital allocations over time.
The yield component makes this product more attractive than a standard spot ETF. Institutional participation in new instruments like this typically accelerates after an initial quiet period.
Shrinking exchange supply is another factor that warrants close attention. As more ETH moves off exchanges into staking or cold storage, available selling pressure decreases.
Combined with ongoing whale activity, this dynamic could produce a supply squeeze if demand continues to build at its current pace.
On-Chain Data Supports the Accumulation Thesis
Crypto analyst CW8900 noted that active Ethereum addresses have risen sharply despite the recent price decline. This trend of rising network activity during a price dip has been consistently observed near Ethereum market bottoms since 2022. The data indicates that participants are using the low-price window to accumulate ETH.
Moreover, the analyst pointed out that activity increased most sharply immediately after the latest price decline. This timing closely mirrors behavior seen during prior Ethereum accumulation phases.
Source: Cryptoquant
It adds weight to the view that experienced market participants are actively positioning at current price levels.
The divergence between price action and network activity is a well-tracked indicator in on-chain analysis. When prices decline while active addresses rise, it often reflects growing engagement from new or returning market participants. This behavior has historically preceded broader market recoveries across past Ethereum market cycles.
That said, price confirmation has not yet arrived. ETH continues to trade within the established range, and no breakout has materialized.
Market participants are closely watching whether this accumulation trend will eventually translate into a sustained price move higher.
The post ETH Whale Accumulation Hits Record Highs as BlackRock Staking ETF Launches on Nasdaq appeared first on Blockonomi.
Ripple just expanded its stablecoin payment infrastructure for banks and fintech companies across the globe, and the XRP price prediction is getting louder. Historical data shows XRP trading in a descending channel from its $3.6 peak, and analysts project a potential rally to $8.6 by Q4 2026 if the pattern breaks.
That sounds impressive until you compare it to listing math. An XRP move from $1.39 to $8.6 delivers roughly a 6x. The presale entry about to list delivers multiples that make 6x look like a savings account. This article covers the XRP outlook and the presale where the listing erases this price forever.
Ripple expanded its stablecoin based payment platform to help banks and fintech companies move money faster reducing foreign reserve requirements according to Coinedition. The upgrade adds stablecoin collection, custody, conversion, and payout across Ripple’s global network.
Separately, historical data reveals XRP’s descending channel from the $3.6 July peak could resolve in a rally to $8.6 between September and December 2026. The XRP forecast benefits from expanding infrastructure, but the listing math at presale pricing makes even a 6x XRP rally look modest.
XRP Price Prediction Targets $8.6, but This Presale Listing Makes Those Returns Look Ordinary
Pepeto: The Listing Erases This Entry Forever and the Clock Is Running Out
The timing on this presale is closing faster than most people realize. While the XRP forecast debates $8.6 by December, Pepeto sits at a fraction of a cent with a listing approaching that will erase this entry permanently. The moment trading begins, this price ceases to exist and the open market decides what an exchange token backed by real infrastructure is actually worth.
That’s how every exchange token listing in crypto history has worked. The presale price is the entry. The listing is the repricing. The gap between those numbers is where wealth gets created, and Pepeto’s gap shrinks with every round that fills.

The cofounder who built Pepe to $7 billion is building the exchange underneath. PepetoSwap handles cross chain swaps with zero fees, a bridge moves assets between networks that normally can’t communicate, and risk scoring checks every token’s safety before you buy. These tools generate the volume that makes exchange tokens valuable after listing, and the Binance listing approaches with every stage that closes.
Staking at 199% APY compounds positions for the wallets already inside, and the listing itself transforms presale entries into open market positions at whatever price the volume demands. Right now, two types of people are reading this. The ones who’ll get into Pepeto before the listing erases this entry, and the ones who’ll look back at this article and wish they’d acted when the math was still in their favor.
XRP Price Prediction: $1.39 in Descending Channel With $8.6 Target if Pattern Breaks
XRP trades near $1.39 according to CoinMarketCap within a descending channel from the $3.6 July 2025 peak, down 23.8% year to date. Historical data suggests a potential rally to $8.6 between September and December 2026 if the channel resolves bullishly.
Seven spot XRP ETFs hold $1.06 billion in total assets, and institutional access continues expanding. But even the most bullish XRP forecast delivers a 6x from here, respectable for a large cap but not the kind of return that changes financial trajectories.
BNB: $656 Exchange Token King but Ground Floor Entry Disappeared Years Ago
BNB trades near $656, proving exchange tokens outperform every cycle. Binance’s ecosystem keeps expanding with over $130 billion in BlackRock crypto products flowing through according to Fintechweekly.
But the ground floor that created BNB millionaires vanished at $0.15. The next BNB sits at presale pricing right now.
XRP Price Prediction Requires Months of Waiting, but This Listing Changes Everything Now
Here’s what regret looks like in crypto: reading about an opportunity, understanding the math, and choosing to wait while others act. XRP’s channel could take months to resolve. The Pepeto listing won’t wait that long.
The cofounder who built $7 billion in demand is building again, the community keeps growing, and the moment trading goes live this price disappears permanently. Visit the Pepeto official website and act while the entry that the listing erases is still available.
Click To Visit Pepeto Website To Enter The Presale

FAQs
What is the XRP forecast for Q4 2026?
The xrp price prediction targets $8.6 by Q4 2026 based on historical channel data, a 6x from current levels, while presale listings like Pepeto offer listing math that operates on a different scale.
How does Ripple’s stablecoin expansion affect the XRP forecast?
Ripple’s stablecoin expansion supports institutional adoption and the bullish XRP forecast, but returns remain limited by XRP’s large cap structure.
Where can I find presale entries with better returns than XRP?
Pepeto offers exchange infrastructure at presale pricing with listing math that dwarfs large cap returns. Visit the Pepeto official website before the listing erases this entry.
The post XRP Price Prediction Points to $8.6 Rally as Ripple Expands Stablecoin Stack, but Pepeto’s Listing Math Could Erase These Returns Before XRP Even Moves appeared first on Blockonomi.
TLDR:
- Coinbase and Bybit are in early-stage investment talks, with no official confirmation from either party yet.
- Bybit’s valuation is estimated at around $25 billion, mirroring ICE’s recent investment deal with OKX.
- The partnership could give Dubai-based Bybit a fully regulated entry point into the US crypto market.
- COIN stock rose 1.18% on the news, gaining nearly 20% over the past month amid rising investor confidence.
Coinbase and Bybit are reportedly in discussions for a major investment deal. The potential partnership could give Dubai-based Bybit a regulated path into the US crypto market.
Three sources confirmed the talks to WuBlockchain, although neither party has officially commented. No final outcome has been reached as of now.
Reports indicate Bybit’s valuation could reach around $25 billion, based on a comparable deal involving OKX and ICE. The deal could also expand Coinbase’s global reach if confirmed.
Coinbase-Bybit Deal Could Open US Market to Offshore Exchange
The current discussions between Coinbase and Bybit cover a broad range of possible cooperation. This includes potential investment and other forms of formal collaboration between the two exchanges. However, the talks remain exploratory, and no binding agreement has been reached yet.
Bybit is the world’s second-largest offshore crypto exchange, headquartered in Dubai. The platform serves a large global user base and offers a wide range of trading products. Gaining a regulated foothold in the US market has been a strategic priority for the exchange.
Coinbase, as the largest US-based crypto exchange, brings deep regulatory experience to the table. Experts say its background in licensing, reporting, and customer protection could benefit Bybit considerably.
Through this partnership, Bybit could navigate US compliance requirements far more effectively. Coinbase’s strong track record with US regulators adds credibility that Bybit would need in the market.
The deal also mirrors other recent strategic moves in the crypto sector. ICE recently invested in offshore exchange OKX at a valuation of $25 billion.
Additionally, Coinbase acquired Deribit last year in a $2.9 billion transaction, reflecting a pattern of expansion through strategic deals.
Industry Response and Market Reaction to the Coinbase-Bybit Reports
Social media has seen a wave of speculation since WuBlockchain first reported the story. On X, OKX founder Star Xu shared his reaction to the reports, stating: “If it’s true, good for the industry. Higher standards, less regulatory arbitrage.” His comment reflects a broader positive sentiment toward regulated collaboration in the crypto space.
Experts note that a successful Coinbase-Bybit deal could benefit both parties in distinct ways. For Coinbase, it offers an expanded global reach and a stronger international presence.
For Bybit, the deal opens a structured and compliant entry into the US market. The partnership could also position both companies more competitively in an evolving global landscape.
The COIN stock price responded positively to the emerging reports. Shares closed at $195.53, recording a 1.18% gain in a single trading day. Over the past month, the stock has risen nearly 20%, pointing to growing investor confidence around Coinbase’s strategic direction.
The talks remain in their early stages, and no official timeline has been confirmed. Both Coinbase and Bybit have yet to release any public statement on the matter. The industry continues to watch closely for further developments as speculation around the deal grows.
The post Coinbase and Bybit in Investment Talks: Could Bybit Finally Enter the US Crypto Market? appeared first on Blockonomi.
CryptoPotato
Bitcoin’s price moves continue to be quite muted despite the most recent developments on the rapidly increasing Middle East tension. After today’s big strikes against a key Iranian island, Trump urged numerous countries to send military ships to defend the oil export through the Strait of Hormuz, and France was among the first to respond positively.
At the same time, Oman officials said they tried to broker a peace deal between the US and Iran, but to no avail.
France Sends Ships
CryptoPotato reported earlier on Saturday that the US military carried out a targeted operation against Iran’s Kharg Island, which the POTUS described as “the most powerful bombing raids in Middle East history.” However, he added that the US intentionally did not attack any oil infrastructure but threatened to do so if Iran interferes in any way with the free and safe passage of ships through the Strait of Hormuz.
Hours later, Trump urged other countries, including China, France, Japan, South Korea, and the UK, to send “Warships” to the region to ensure the Strait remains open and safe. Reports from minutes ago suggested that France concurred with the US President’s message, sending 10 warships to the region. However, the UK has refused to deploy any military aircraft carriers as of press time.
In a separate development on the matter, The Kobeissi Letter reported that Russia has become the first nation to aid Iran in some official way after the war began, sending 13 tons of medical aid.
No Peace Deal Yet
Another report that just came out indicated that officials from Oman have “reached out to the US in an attempt to broker a peace deal with Iran,” but the US President declined.
Some of the details on the matter suggest that Oman has tried “multiple times” to open a line of communication, but the White House was “not interested.” According to a cited senior official from the Trump administration, the President is “focused on pressing ahead with the war.”
BREAKING: Oman has reached out to the US in an attempt to broker a peace deal with Iran, but President Trump declined, per Reuters.
Details include:
1. Oman has tried “multiple times” to open a line of communication, but the White House is “not interested”
2. A senior White…
— The Kobeissi Letter (@KobeissiLetter) March 14, 2026
Bitcoin’s price continues to be unaffected by these developments, trading above $70,000 as of press time. However, the asset has historically dumped after most financial markets open on late Sunday and early Monday.
The post BTC Wobbles at $70K as France Deploys Ships to Hormuz and Trump Rejects Peace Deal Attempt (Report) appeared first on CryptoPotato.
Ethereum is still in recovery mode, but the rebound is starting to look more organized than before. The asset continues to hold above the February base and is pressing closer to a key breakout area, which suggests buyers are gradually gaining confidence even if the larger trend has not fully turned yet.
Ethereum Price Analysis: The Daily Chart
The daily chart still carries the scars of the broader downtrend. ETH remains below the 100-day and 200-day moving averages, and both are still sloping in a way that favors sellers on the higher timeframe. The descending structure from the prior months also remains intact, so the market is not out of danger yet.
Even so, the picture has improved at the margin. Ethereum has spent several weeks defending the $1,800 zone and has now pushed back toward the $2,150 short-term resistance area again. If that ceiling breaks, the next upside region to watch sits around $2,300 to $2,400, while the much larger barrier remains near $2,800. On the downside, losing the $1,800 support cluster would weaken the recovery thesis considerably and likely lead to another round of decline capitulation.
ETH/USDT 4-Hour Chart
On the 4-hour chart, ETH looks more constructive than it does on the daily. The market has been printing a sequence of higher lows from the February bottom, and the rising trendline underneath the price shows that dip buyers are still active. That does not guarantee a breakout, but it does show that the short-term structure is leaning upward rather than flat or weak.
What matters now is the repeated test of $2,143. The asset has reached that level several times, which usually makes the next reaction important. A decisive move through it could trigger a fast push into the next supply zone around $2,400 and possibly higher. Another rejection, however, would likely keep ETH rotating sideways and send it back toward the trendline and the $1,800 support area.

Sentiment Analysis
Funding data shows that sentiment is no longer fearful, but it is not overheated either. Rates are mostly positive, which means long positioning is present, and traders are generally leaning bullish, yet the readings are still relatively moderate compared to the stronger speculative phases seen in the past.
That is usually a healthier backdrop than an aggressively crowded long market. In other words, sentiment is supportive, but not euphoric. This gives ETH room to extend higher if price confirms with a breakout, though it also means the market still needs spot follow-through rather than relying purely on leveraged optimism.

The post Ethereum Price Prediction: Can ETH Launch a Strong Rebound After Reclaiming $2K? appeared first on CryptoPotato.
The popular Chinese crypto news channel Wu Blockchain reported earlier today that two of the industry’s giants, Coinbase and Bybit, are in talks for some sort of investment partnership.
Although the currently available information is quite limited and there’s no official response from either party, it’s reported that Bybit’s valuation could match OKX’s after the most recent funding event.
Exclusive: Coinbase, the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the US, is in talks with Bybit, the world’s second-largest offshore exchange, for an investment partnership. Bybit hopes to use this opportunity to enter the compliant US market. Three sources confirmed this news to… pic.twitter.com/SXBJnbDOQG
— Wu Blockchain (@WuBlockchain) March 14, 2026
Citing three sources that confirmed the information, the report further indicated that such a collaboration would enable Bybit to enter the compliant US market.
It would follow several notable deals in the cryptocurrency space, such as Coinbase’s acquisition of the derivatives giant Deribit. As reported during the summer of 2025, the Wall Street-listed exchange purchased Deribit for $2.9 billion as the derivatives market was exploding.
More recently, OKX received a massive nod from the Intercontinental Exchange. The entity behind the New York Stock Exchange acquired a minority stake in the cryptocurrency exchange, putting its valuation at an impressive $25 billion following the latest investment round.
According to Wu Blockchain, Bybit’s valuation should be similar to OKX’s, meaning somewhere around $25 billion.
CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko data show that all three trading platforms – Coinbase, OKX, and Bybit – are placed within the top five of their trust lists, with some of the highest scores in the industry.
The post Coinbase and Bybit in Talks for Strategic Investment Partnership: Report appeared first on CryptoPotato.
The demand for the spot XRP ETFs in the United States has seemingly evaporated as the funds have not seen a single day of net inflows for over one whole week.
Nevertheless, the underlying token managed to post some gains over the past week before it was halted at $1.45.
XRP ETFs See Investor Exodus
The exchange-traded funds tracking the performance of the cross-border token enjoyed their initial honeymoon period that lasted roughly a month, in which they attracted over $1 billion in cumulative net flows. However, they began to slowly disappear from investors’ radar. The first two warning signs were observed on January 7 and 20 when $40.80 million and $53.32 million were pulled out of the funds.
January ended with another mass withdrawal of $92.92 million on January 29, and the overall month was just slightly in the green – $15.59 million; a figure significantly lower than the $666.61 million seen in November and $500 million in December.
February picked up the pace, as the total monthly inflows stood at $58.09 million. However, more warning shots were seen as there were days with zero net inflows. Such trading days returned in the previous week – SoSoValue shows $0.00 reportable inflow data for March 11 and March 13. Moreover, the other three trading days were in the red, with $18.11 million leaving the funds on Monday, $3.88 million on Tuesday, and $6.08 million on Thursday.
This negative streak extends to the previous business week. In fact, the funds have not seen a green day since March 4.
XRP Price Ascent Halted
Despite the investor exodus, XRP’s price fared rather well in the past week, jumping from a Monday low of $1.34 to a multi-week peak of just over $1.45. However, it was stopped there and now struggles below $1.40.
Its most recent price moves have been contained in a relatively tight trading range, which has prompted many analysts to suggest that there’s a big move in the making. Ali Martinez, for example, noted a few days ago that XRP’s Bollinger Bands have been squeezing, hinting at a major breakout soon.
He doubled down earlier today, saying that XRP’s current triangular consolidation is approaching its tipping point, with a 30% price move brewing.
$XRP is consolidating in a triangle, hinting at a 30% price move. pic.twitter.com/lgjOWKUBHU
— Ali Charts (@alicharts) March 14, 2026
The post Zero Net Inflows All Week: Ripple (XRP) ETFs Lose Investor Momentum appeared first on CryptoPotato.
Popular analyst Merlijn The Trader outlined in a recent post on X that bitcoin’s current setup resembles, to a large extent, its market behavior in late 2022 when the asset actually skyrocketed by triple digits from bottom to top.
To even have the theoretical chance of doing so, though, Merlijn outlined the key level BTC has to hold.
385% Surge in the Making?
His analysis noted that bitcoin had already run this playbook over three years ago, which is evident from the descending compression and sweep buy liquidity. He believes this setup will trap late sellers and BTC’s price will eventually reverse upon its conclusion.
Merlijn explained that the last time this happened, BTC’s price skyrocketed from $15,000 to $73,000. A similar price surge of 385% would send the cryptocurrency flying to well over $300,000.
Obviously, such a scenario is hard to envision now and might sound like a stretch, but Merlijn indicated that BTC could reignite a highly impressive rally as long as it holds the key $65,000 level. If it doesn’t, then it would continue the liquidity sweep phase.
BITCOIN RAN THE SAME PLAYBOOK AS NOVEMBER 2022.
Descending compression. Sweep buy liquidity.
Trap late sellers. Then reverse.Last time this resolved: BTC went from $15K to $73K.
Hold $65K: base is complete.
Lose it: liquidity sweep continues.The market hunts liquidity… pic.twitter.com/BDPICGhWYS
— Merlijn The Trader (@MerlijnTrader) March 14, 2026
He doubled down in a subsequent post that every major BTC cycle had started with a bear trap. In previous examples, such as the massive runs in 2013, 2016, and 2020, the price gains were quite spectacular – 24,000%, 6,300%, and 842%, respectively.
The analyst noted that the pattern doesn’t change as fear is always the first phase of the rally. And, as reported recently, fear has dominated the crypto market for a few consecutive months.
Still Bear Cycle
In the meantime, Doctor Profit, among the most well-known crypto analysts who have been calling for this correction for months, acknowledged BTC’s recent pump to $74,000. However, he argued that this is likely to be a short-term upside move, before “we see another downturn” to new lows.
The cryptocurrency was indeed rejected at $74,000 for the second time in the past 10 days or so, and now struggles to remain above $70,000.
#Bitcoin is rising fast and strong, exactly as predicted. Expect more upside move before we see another downturn move to new lows. In the meantime, let’s enjoy the fake pump together that will last for some weeks!
— Doctor Profit
(@DrProfitCrypto) March 13, 2026
The post Bitcoin’s Price Is Running the Same Playbook That Led to a 400% Surge But There’s a Catch appeared first on CryptoPotato.

 pic.twitter.com/ncI3GCyebq
pic.twitter.com/ncI3GCyebq










 IOTA is already testing something that could change how RWA are financed.
IOTA is already testing something that could change how RWA are financed.































